DevSecOps Process Management
Covers eight core processes that span the software delivery lifecycle. Each process includes implementation details for different organizational contexts.
DevOps Process Management: The Complete Enterprise Guide
DevOps process management sits at the intersection of speed and security. Organizations pushing code to production multiple times per day face a fundamental challenge: maintaining security controls without becoming deployment bottlenecks. The average enterprise runs 247 different tools across their DevOps pipeline, creating complexity that attackers actively exploit.
This guide examines DevOps process management through two lenses. First, we document how production teams actually implement these processes across legacy infrastructure, hybrid clouds, and cloud-native platforms. Second, we analyze attack patterns where adversaries compromised these same processes to breach organizations.
What you’ll find here:
The article covers eight core processes that span the software delivery lifecycle. Each process includes implementation details for different organizational contexts startups running Kubernetes clusters need different approaches than banks maintaining mainframe systems. We’ve documented both automated and manual variants because the reality is most organizations operate somewhere between these extremes.
You’ll see specific attack scenarios covering missing approval gates, unrotated secrets, and skipped security scans that led to production compromises. Each attack includes the technical steps adversaries followed and the process controls that would have prevented them.
The metrics matter. We’ve included KPIs for every process step because “implement security scanning” means nothing without measuring scan duration, false positive rates, and developer remediation times. These numbers come from actual implementations, not aspirational targets.
This pattern repeats across industries. The tools change, the cloud providers vary, but the failure mode stays consistent—process shortcuts that seem reasonable under deadline pressure become attack vectors.
1. The 3:47 AM Incident: When Process Fails
Quick Reference: Incident Response Flow
Detection → Initial Discovery → Impact Assessment → Root Cause → Timeline Analysis → Cost Calculation → Lessons Learned
1.1 Incident Overview
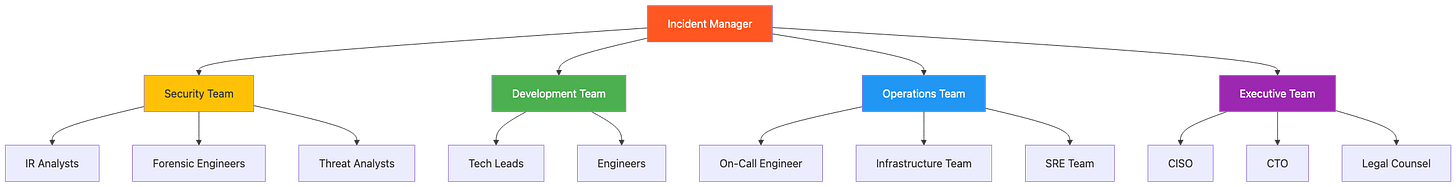
Incident Response Team Structure:
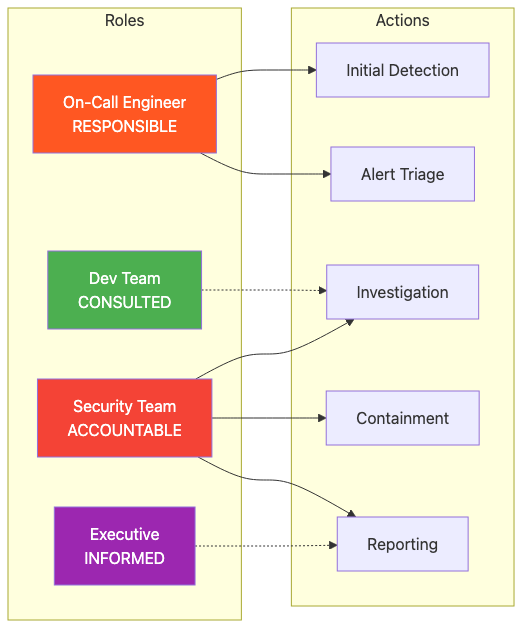
Incident Response RACI Matrix:
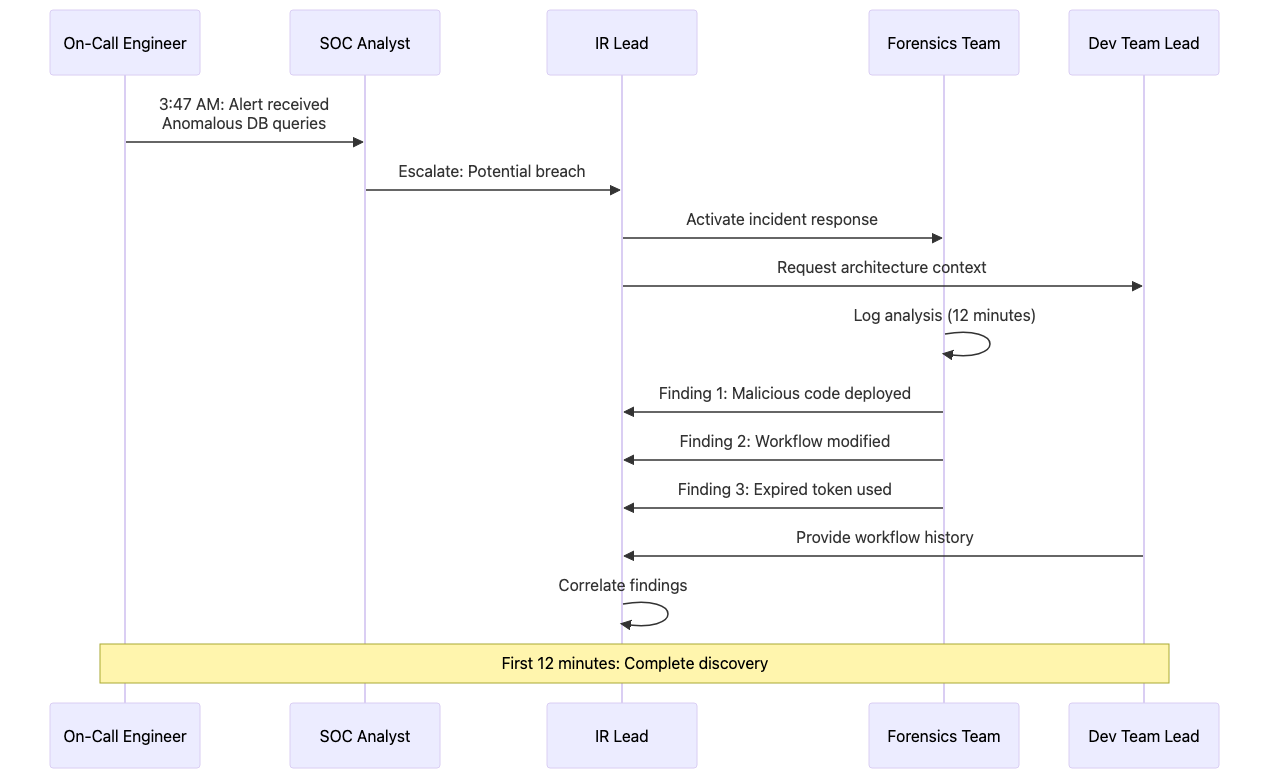
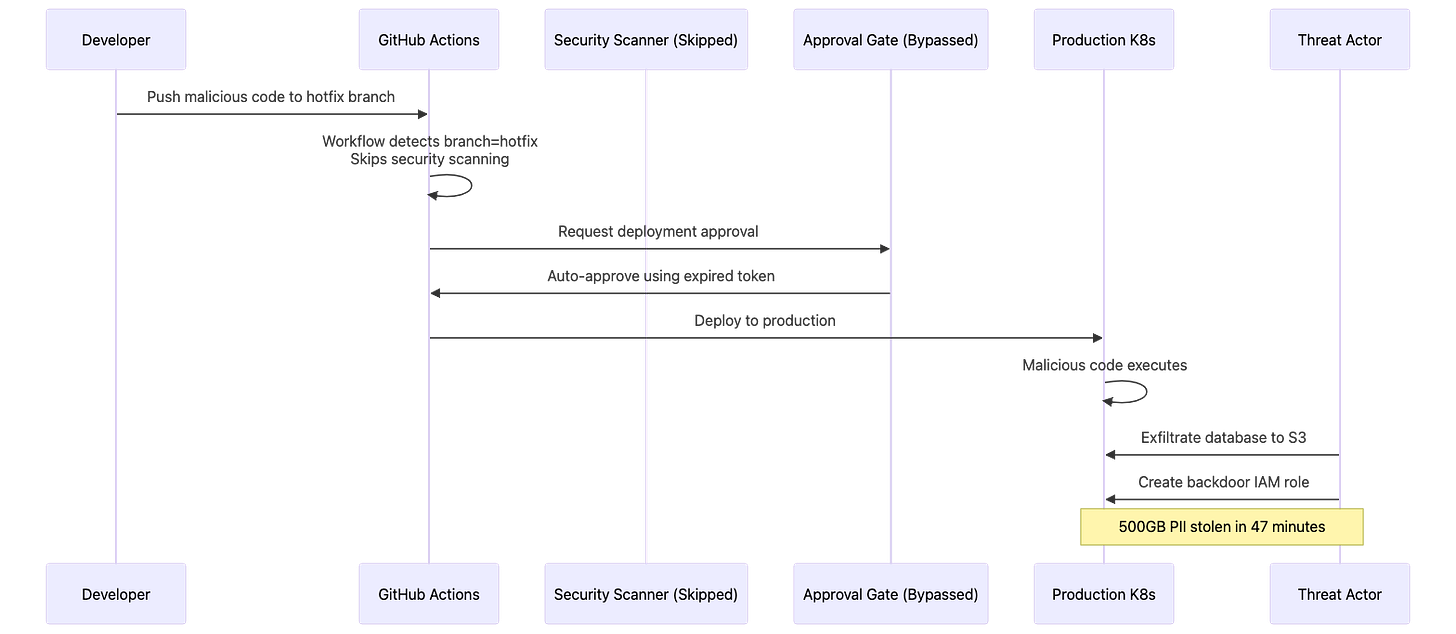
A global SaaS provider serving 2 million users experienced a production security breach during off-hours. The on-call engineer received alerts at 3:47 AM showing anomalous database queries against the production payment processing system.
1.2 Initial Discovery
Investigation Cheatsheet:
Step 1: Alert Triage → Step 2: Log Analysis → Step 3: Access Review → Step 4: Configuration Audit → Step 5: Impact Scope
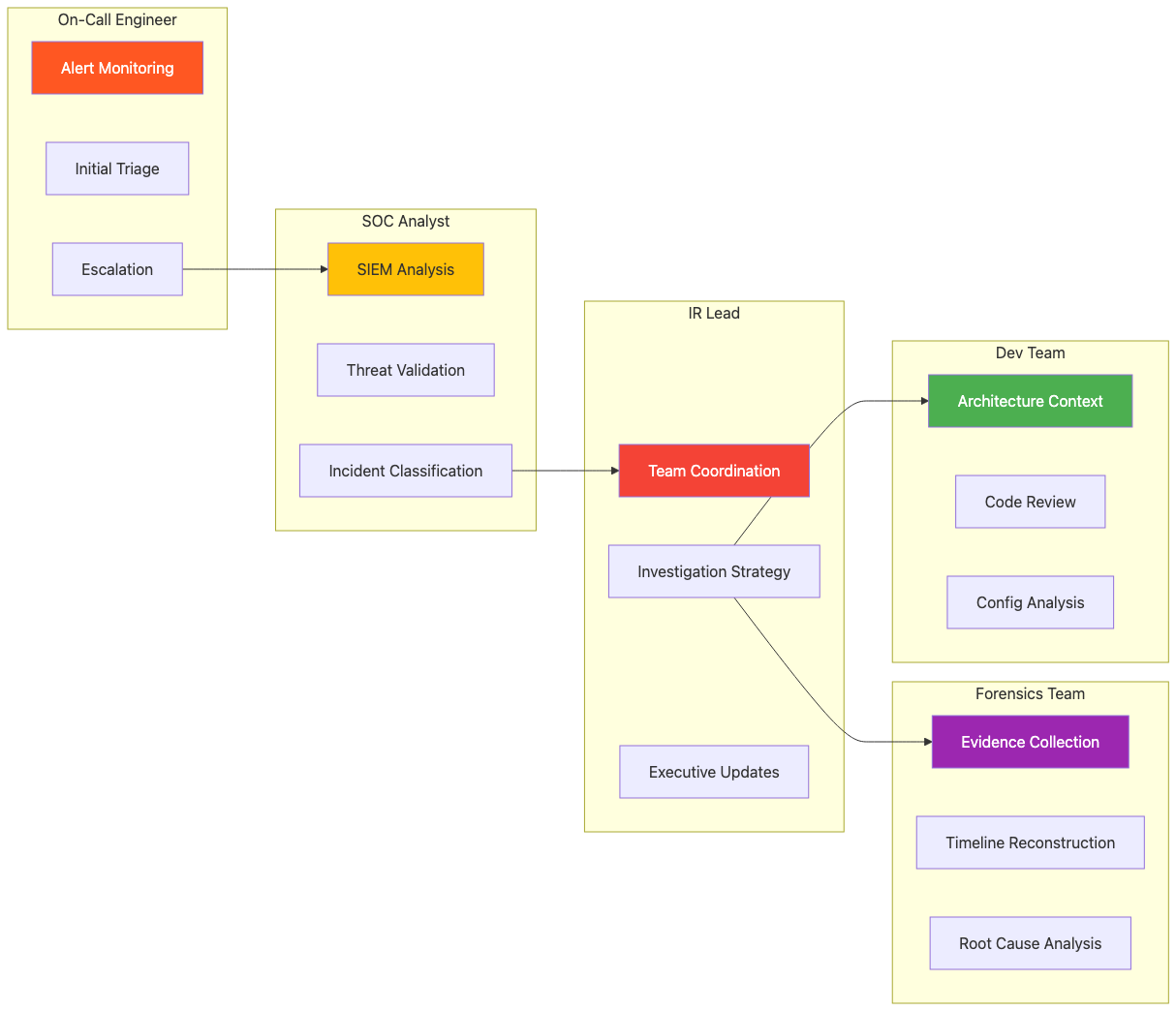
Investigation Team Collaboration:
Investigation Roles & Responsibilities:
Within the first 12 minutes of investigation, the security team identified several alarming indicators. Malicious code had been deployed to production through a “hotfix” branch that bypassed normal review processes. The GitHub Actions workflow configuration had been modified to skip the security scanning stage entirely. An expired service account token, which should have been rotated months earlier, provided the authentication needed to bypass the approval gate.
1.3 Breach Impact Assessment
Damage Assessment Steps:
Data Exfiltration Analysis → Backdoor Detection → Privilege Escalation Review → Lateral Movement Tracking → Persistence Mechanisms
The attackers moved quickly once inside the production environment. They exfiltrated 500GB of customer personally identifiable information to an S3 bucket under their control. To maintain persistent access, they created a backdoor IAM role with administrative privileges that would survive the immediate incident response.
1.4 Root Cause Analysis
RCA Process Flow:
Symptom Identification → Timeline Reconstruction → Configuration Review → Process Gap Analysis → Control Failure Mapping
The deployment process fundamentally lacked mandatory security checkpoints. A developer, facing pressure to resolve a critical bug affecting paying customers, created a modified workflow file. This workflow treated the “hotfix” branch as a special case that could skip security validation. The change merged and deployed to production within 8 minutes—fast enough to avoid human oversight but slow enough that automated detection systems failed to flag the anomaly.
1.5 Attack Timeline
Attack Chain Steps:
Initial Access → Workflow Modification → Security Bypass → Deployment → Code Execution → Data Exfiltration → Persistence
The entire attack sequence from initial code push to data exfiltration completion took 47 minutes. The attackers had clearly studied the organization’s deployment process and understood exactly which shortcuts existed in the workflow configuration.
1.6 Financial and Operational Impact
Cost Breakdown Flow:
Impact Analysis by Stage:
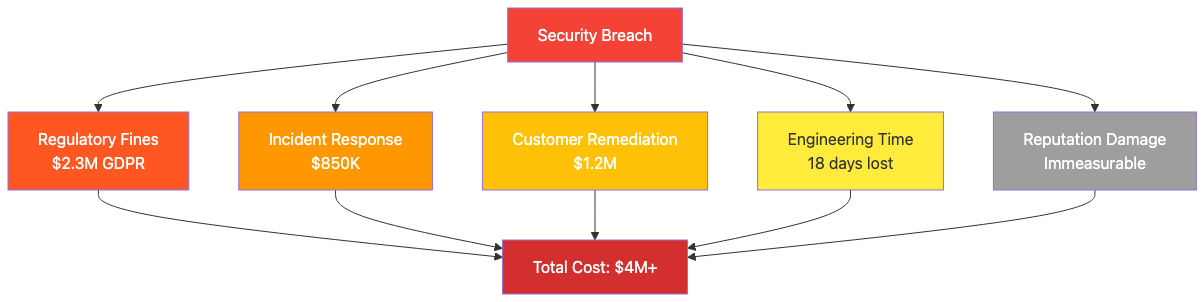
Regulatory Fines — $2.3M in GDPR penalties for exposing 500GB of customer PII without adequate security controls
Incident Response — $850K for forensic investigation, external security consultants, and emergency remediation
Customer Remediation — $1.2M for credit monitoring services, legal settlements, and customer support infrastructure
Engineering Time — 18 days of lost productivity across security, DevOps, and development teams rebuilding compromised systems
Reputation Damage — Immeasurable long-term impact on customer trust, brand value, and competitive positioning
1.7 The Single Point of Failure
Single Line of Code Impact:
Root Cause Analysis:
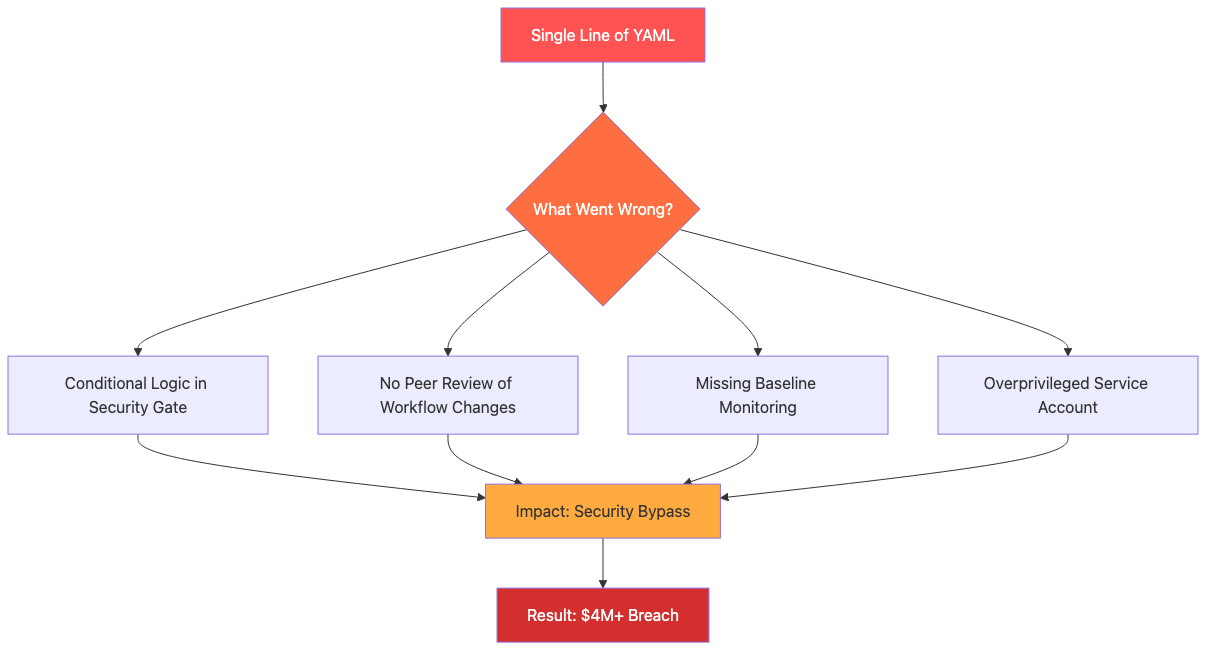
One missing security gate in a CI/CD process created the vulnerability that enabled this entire incident. The workflow file contained a conditional statement that said “if branch equals hotfix, skip security scanning.” That single line of YAML configuration cost the company over $4M and immeasurable reputational damage.
This article documents the processes, controls, and detection mechanisms that prevent organizations from experiencing their own 3:47 AM incident.
2. DevOps Process Architecture: Secure vs. Insecure
Architecture Comparison Flow:
2.1 Common Insecure Process Patterns
Most organizations inherit process anti-patterns through organic growth rather than intentional design. A startup’s quick-and-dirty deployment script becomes the enterprise’s production process three years later. These patterns create exploitable gaps that attackers actively target:
2.1.1 Manual Approval Gates
Risk Flow Diagram: