Investigate Incident with Logs like Ninja
dev/sec/ops important services logs
Your phone buzzes. Slack alert from PagerDuty: “CRITICAL: Unauthorized deployment to production EKS cluster.” You’re wide awake now.
The timeline unfolds rapidly:
3:17 AM: Deployment triggered from Jenkins—but no one’s on shift
3:18 AM: ArgoCD syncs Terraform changes to production AWS resources
3:19 AM: Falco alerts on suspicious container spawning
/bin/shwith root privileges3:22 AM: AWS CloudTrail shows IAM role assumption from unknown IP
203.0.113.473:25 AM: Prometheus metrics spike—CPU usage jumps 400%
You open your laptop, terminal blinking in the darkness. Where do you start?
Most engineers panic-check Kubernetes logs. The attacker knows this. They’ve already tampered with:
Jenkins build logs (deleted pipeline execution history)
GitHub Actions audit logs (forged commit metadata)
AWS CloudTrail (disabled logging for 47 minutes)
Docker container logs (injected fake timestamps)
But you’re different. You investigate incidents like a ninja—correlating logs across 44 technologies, detecting anomalies attackers can’t hide, and reconstructing the full kill chain.
This is your playbook.
Insecure Log Architecture: The Attacker’s Playground
What Makes This Architecture Vulnerable?
1. Decentralized Log Storage
Jenkins logs stored on master node—single point of failure
Kubernetes logs on ephemeral node disks—lost on pod eviction
AWS CloudTrail writes to S3—attacker can pause/delete trail
Application logs in container filesystems—destroyed on restart
2. No Immutable Audit Trail
Logs are mutable files attackers can edit with
sed,awk, or direct writesNo cryptographic verification—timestamps can be forged
Missing log forwarding—evidence disappears with compromised systems
3. Insufficient Access Controls
Jenkins admin can delete build history via UI
Kubernetes node access allows direct log file manipulation
S3 bucket policies lack
s3:PutBucketLoggingdeny rulesNo separation of duties—engineers have delete permissions
Real-World Impact: In the SolarWinds breach (2020), attackers modified build logs to hide malicious code injection. The tampering went undetected for months because logs were stored locally on compromised build servers.
Secure Log Architecture: The Ninja’s Fortress
Defense-in-Depth Principles
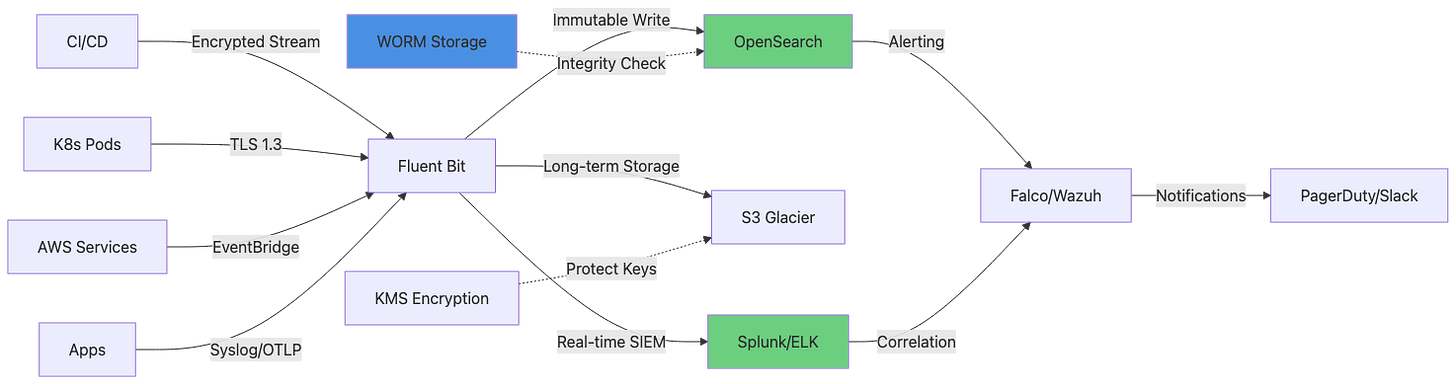
1. Centralized Immutable Collection
Fluent Bit/Fluentd agents forward logs in real-time via TLS 1.3
Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) storage prevents tampering
Cryptographic signatures on log entries using HMAC-SHA256
Multi-region replication to S3 buckets with MFA Delete enabled
2. Separation of Log Plane
Dedicated log infrastructure—isolated VPC/network segment
Least privilege access—engineers cannot delete production logs
API-only modifications with full audit trail (who, what, when)
Air-gapped backup to offline storage every 24 hours
3. Real-Time Correlation & Alerting
SIEM platforms (Splunk, ELK, Datadog) aggregate 44 sources
Behavioral baselines—detect anomalies via ML (Prometheus, Grafana)
Cross-reference events—link GitHub commit → Jenkins build → K8s deploy
Automated response—Falco triggers pod quarantine on suspicious behavior
Attack Techniques: Multi-Stage Log Evasion
Team Roles & Responsibilities Across All 44 Technologies
Role Definitions:
SOC Analyst: Monitors 44 log sources, investigates alerts from SIEM/Falco/Wazuh, performs threat hunting across Slack/Teams/GitHub/AWS, responds to security incidents
DevOps Engineer: Manages CI/CD pipelines (GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI), deploys to K8s/Docker, provisions infrastructure via Terraform/Ansible, configures Fluent Bit agents
Security Engineer: Defines security policies, configures Falco/Wazuh rules, audits Vault/Secrets Manager access, reviews code in GitHub/GitLab, sets up detection rules
Platform Engineer: Maintains Kubernetes clusters, configures Istio/Linkerd service mesh, optimizes Prometheus/Grafana dashboards, manages cloud infrastructure
SRE: On-call for production incidents, capacity planning in AWS/GCP/Azure, reliability engineering for CI/CD pipelines, SLO/SLI monitoring
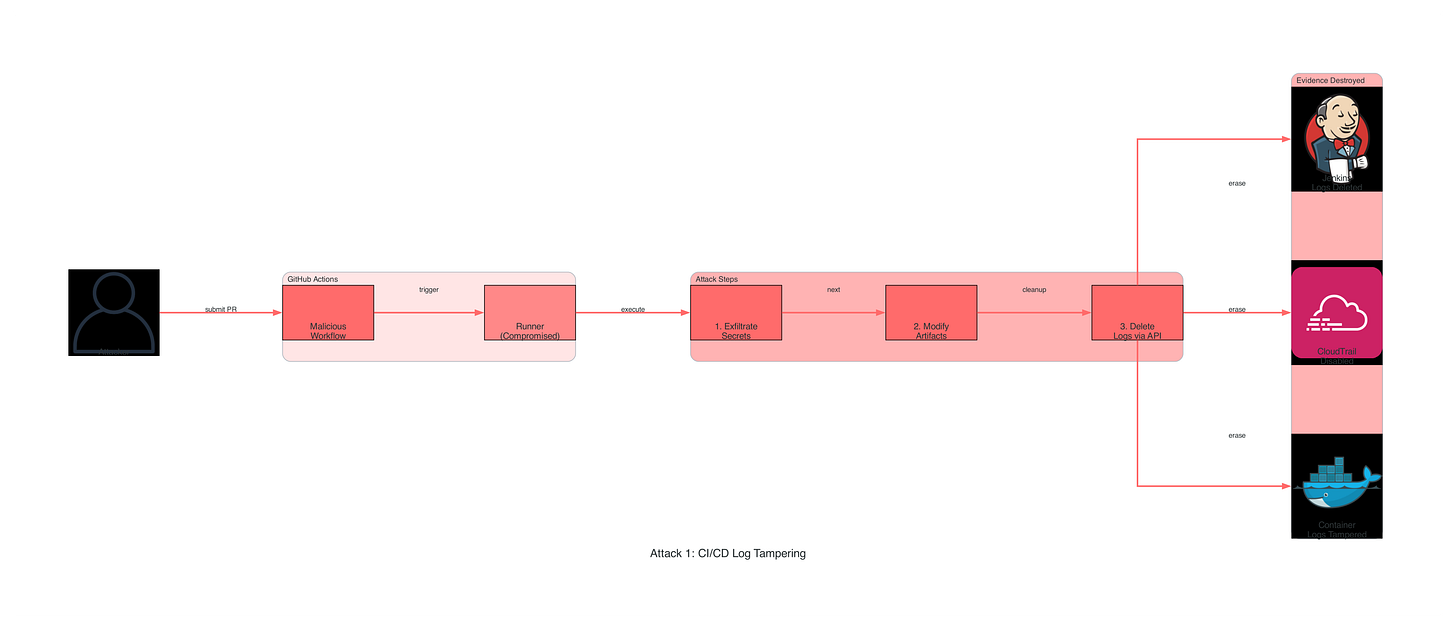
Attack Technique #1: CI/CD Log Tampering (T1562.008)
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Tactic: Defense Evasion
Technique: T1562.008 - Impair Defenses: Disable Cloud Logs
Sub-Technique: Modify/Delete CI/CD Pipeline Logs
The Attack Scenario
An attacker compromises a GitHub Actions runner via a malicious pull request. They inject a workflow step that: